Understanding Keto Cycling: Advantages, Challenges, and Implementation
Introduction to Keto Cycling
Keto cycling represents an evolved approach to the conventional ketogenic diet, tailored to enhance its sustainability through periodic carbohydrate intake. This methodology is aimed at those who find the rigorous carbohydrate restrictions of the traditional keto diet daunting. By integrating higher-carb days, keto cycling offers a more flexible dietary pattern that can help maintain the metabolic benefits of ketosis while allowing for occasional indulgences that make the diet easier to adhere to over the long term.
Difference Between Keto Cycling and Standard Keto Diet
The standard ketogenic diet requires strict adherence to a high-fat, low-carbohydrate regimen to sustain a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat as its primary source of energy. In contrast, keto cycling modifies this strict regime by interspersing days of higher carbohydrate intake. This not only makes the diet more manageable but also helps dieters avoid the common pitfalls of long-term carb restriction, such as nutrient deficiencies, decreased fiber intake, and social isolation during meals.
What Is Keto Cycling?
Defining Keto Cycling
Keto cycling is a strategic alteration to the ketogenic diet wherein individuals alternate between standard keto days and higher-carb days. This approach aims to maintain the benefits of ketosis, like improved blood sugar control and fat loss, while providing leeway in the diet. This cycling process helps mitigate some of the intense restrictions of the ketogenic diet, potentially leading to better adherence and less dietary fatigue.
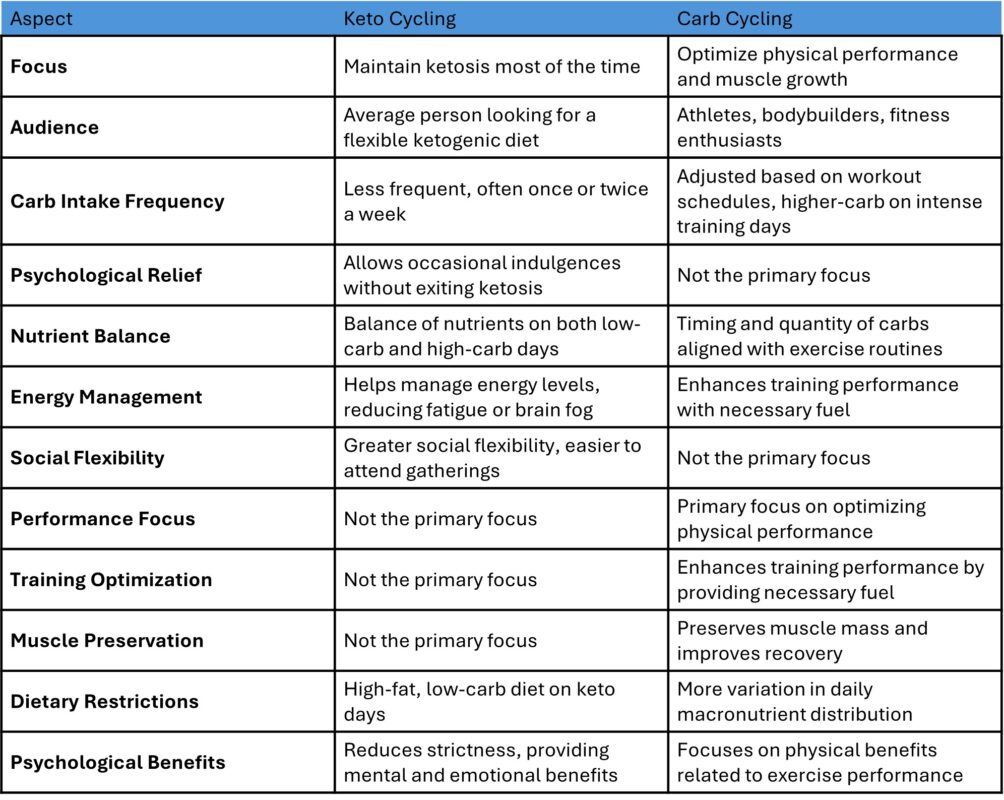
How It Differs from Carb Cycling
While both keto cycling and carb cycling involve fluctuations in carbohydrate intake, their objectives and applications differ significantly. Carb cycling is primarily used by athletes and bodybuilders to optimize physical performance and muscle growth, strategically increasing carbs on workout days. On the other hand, keto cycling is generally aimed at the average person following a ketogenic diet who seeks to lessen the rigidity of maintaining constant ketosis. It offers psychological relief and social flexibility without completely undermining the metabolic state of ketosis.
Origins of Keto Cycling
Historical Background
Keto cycling does not have deep historical roots like the traditional ketogenic diet, which was originally developed in the 1920s as a treatment for epilepsy. The adaptation of keto cycling is relatively recent, developed as a response to the challenges many faced with strict adherence to the ketogenic diet over prolonged periods.
Evolution into Modern Diet Practices
Modern dietary trends increasingly favor flexibility and personalization, characteristics embodied by keto cycling. This practice caters to the contemporary dieter’s need for a balanced approach to eating that accommodates social occasions and fluctuating dietary preferences while still enjoying the benefits of a primarily ketogenic regimen. As dietary science advances, so does the understanding that rigid diet plans can often lead to burnout and relapse. Keto cycling addresses these issues by allowing for dietary “breaks” that help sustain overall commitment to health and wellness goals.
Keto cycling represents a significant evolution in how ketogenic diets are practiced. By allowing for periodic carbohydrate reintroduction, it acknowledges the psychological and social challenges of dietary restrictions and offers a practical solution that can be tailored to individual needs. This approach not only broadens the appeal of the ketogenic diet but also encourages a more balanced and sustainable approach to health and nutrition.
How Keto Cycling Works
The Basics of Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet is fundamentally a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that pushes the body into a state of ketosis—a metabolic state where fat is burned for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Under typical conditions, the body relies on glucose from carbohydrates as its primary energy source. When carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, the body shifts to breaking down fats, producing ketone bodies that serve as an alternative energy source. This metabolic shift is central to the keto diet’s effectiveness in fat loss and improved metabolic health.
Introducing Carbs: The Keto Cycling Method
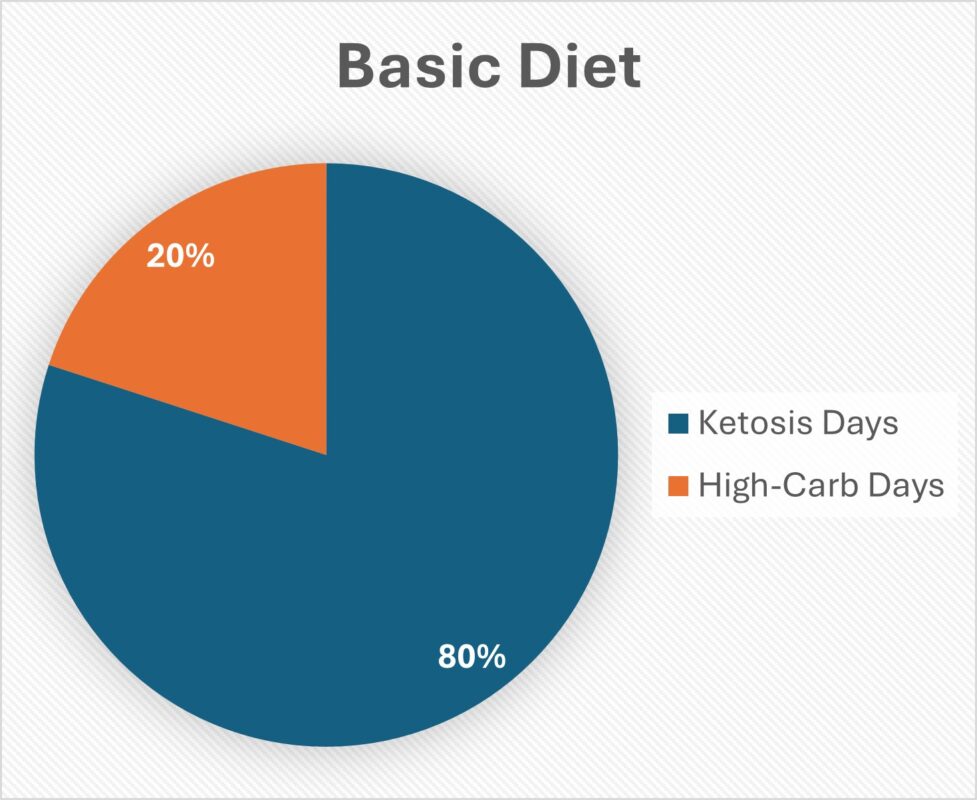
Keto cycling modifies the traditional keto diet by allowing for scheduled high-carb days. This variation aims to offer a reprieve from the potential long-term monotony and restrictions of continuous ketosis. During high-carb days, the body temporarily exits ketosis, which can help manage some of the common side effects associated with a prolonged state of ketosis, such as fatigue, constipation, or mood swings. After the high-carb phase, the dieter returns to the standard keto regimen, ensuring that ketosis is maintained most of the time while still enjoying the metabolic flexibility.
Potential Benefits of Keto Cycling
Increased Flexibility in Diet
One of the primary advantages of keto cycling is its increased dietary flexibility. This adaptability can make it more appealing and sustainable for individuals who find the strict nature of the traditional ketogenic diet challenging. The ability to incorporate higher-carb foods occasionally can help alleviate dietary boredom and improve adherence, which is crucial for long-term success.
Enhanced Physical Performance
Another significant benefit of keto cycling is the potential enhancement in physical performance. On high-carb days, the increase in carbohydrate intake can replenish glycogen stores, which is essential for energy during high-intensity workouts. This can be particularly beneficial for athletes who might struggle with energy levels on a strict keto diet. Additionally, cycling carbohydrates can help maintain muscle mass, as glycogen is critical for muscle recovery and growth.
Overall, keto cycling offers a balanced approach that mitigates some of the stringent aspects of the ketogenic diet, making it a more practical choice for those seeking flexibility in their dietary regimen without sacrificing the benefits of ketosis.
Mental and Emotional Benefits
Psychological Relief from Strict Keto
Keto cycling can provide significant psychological benefits by reducing the mental strain associated with maintaining a strict ketogenic diet. The flexibility to include higher-carb days allows individuals to enjoy a wider variety of foods, which can reduce feelings of deprivation and dietary burnout. This occasional break from strict keto can make it easier for dieters to attend social events and share meals with family and friends, which is often a challenge with restrictive diets. This social integration can boost mental health and emotional well-being, making the diet feel less like a punishment and more like a manageable lifestyle choice.
Impact on Mental Health
Beyond easing social interactions, the mental health benefits of keto cycling include better mood stability and decreased feelings of dietary restriction. Constantly being in a state of ketosis can sometimes lead to irritability and mood swings, often referred to as the “keto flu.” By cycling in higher-carb days, individuals may experience fewer mood fluctuations and a greater sense of overall well-being. This balance can help maintain motivation and commitment to dietary goals, reducing the risk of emotional eating or diet abandonment.
Drawbacks of Keto Cycling
Possible Challenges and Side Effects
While keto cycling offers many benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the main drawbacks is the complexity of managing this diet effectively. The transition between ketosis and higher-carb days requires careful planning to avoid negative side effects such as weight gain and disrupted metabolic health. If not managed properly, the oscillation between different metabolic states can lead to confusion and inconsistency in the body’s metabolic responses, potentially diminishing the benefits of ketosis.
Difficulty in Maintaining Ketosis
Another significant challenge is the difficulty in re-entering ketosis after a high-carb day. This process can be physically uncomfortable and may deter dieters from sticking to the schedule. Symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and gastrointestinal discomfort are common as the body readjusts to ketosis, which can discourage adherence to the cycling schedule.
Nutritional Considerations
Important Nutrients and How to Incorporate Them
Keto cycling requires careful attention to nutritional balance to ensure that dieters receive all essential nutrients. On low-carb days, it’s crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods that are high in fat and moderate in protein, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens, to maintain energy levels and nutritional intake. On high-carb days, selecting complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can maximize nutritional benefit without causing rapid spikes in blood sugar.
Managing Macronutrient Intake
Effectively managing macronutrient intake is key to successful keto cycling. Dieters must understand how to adjust their fat, protein, and carbohydrate intake depending on their daily goals. On low-carb days, fats should predominantly provide the caloric intake, while on high-carb days, the focus shifts to carbohydrates with a reduction in fat consumption. This balancing act is critical not only for maintaining ketosis but also for achieving overall health objectives such as weight loss, muscle gain, or improved metabolic health.
In summary, while keto cycling can offer a more flexible and psychologically sustainable approach to the ketogenic diet, it requires careful planning and consideration of potential drawbacks. Understanding how to navigate the mental, emotional, and nutritional challenges is essential for anyone considering this dietary approach.

Summary
Keto cycling offers a flexible alternative to the traditional ketogenic diet, allowing for periodic high-carb days to ease strict low-carb limitations. This approach enhances dietary adherence and reduces the psychological strain of constant ketosis, making it a sustainable option for long-term health goals. However, it requires careful planning to manage nutritional intake and ketosis transitions effectively. Ultimately, keto cycling caters to modern dietary preferences for flexibility, presenting a balanced solution for those seeking both the benefits of ketosis and a varied diet.







